Saturday, 28 October 2017
BMI
Body Mass Index Table
Body Mass Index Table 1 of 2
| Normal | Overweight | Obese | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| Height
(inches) |
Body Weight (pounds) | ||||||||||||||||
| 58 | 91 | 96 | 100 | 105 | 110 | 115 | 119 | 124 | 129 | 134 | 138 | 143 | 148 | 153 | 158 | 162 | 167 |
| 59 | 94 | 99 | 104 | 109 | 114 | 119 | 124 | 128 | 133 | 138 | 143 | 148 | 153 | 158 | 163 | 168 | 173 |
| 60 | 97 | 102 | 107 | 112 | 118 | 123 | 128 | 133 | 138 | 143 | 148 | 153 | 158 | 163 | 168 | 174 | 179 |
| 61 | 100 | 106 | 111 | 116 | 122 | 127 | 132 | 137 | 143 | 148 | 153 | 158 | 164 | 169 | 174 | 180 | 185 |
| 62 | 104 | 109 | 115 | 120 | 126 | 131 | 136 | 142 | 147 | 153 | 158 | 164 | 169 | 175 | 180 | 186 | 191 |
| 63 | 107 | 113 | 118 | 124 | 130 | 135 | 141 | 146 | 152 | 158 | 163 | 169 | 175 | 180 | 186 | 191 | 197 |
| 64 | 110 | 116 | 122 | 128 | 134 | 140 | 145 | 151 | 157 | 163 | 169 | 174 | 180 | 186 | 192 | 197 | 204 |
| 65 | 114 | 120 | 126 | 132 | 138 | 144 | 150 | 156 | 162 | 168 | 174 | 180 | 186 | 192 | 198 | 204 | 210 |
| 66 | 118 | 124 | 130 | 136 | 142 | 148 | 155 | 161 | 167 | 173 | 179 | 186 | 192 | 198 | 204 | 210 | 216 |
| 67 | 121 | 127 | 134 | 140 | 146 | 153 | 159 | 166 | 172 | 178 | 185 | 191 | 198 | 204 | 211 | 217 | 223 |
| 68 | 125 | 131 | 138 | 144 | 151 | 158 | 164 | 171 | 177 | 184 | 190 | 197 | 203 | 210 | 216 | 223 | 230 |
| 69 | 128 | 135 | 142 | 149 | 155 | 162 | 169 | 176 | 182 | 189 | 196 | 203 | 209 | 216 | 223 | 230 | 236 |
| 70 | 132 | 139 | 146 | 153 | 160 | 167 | 174 | 181 | 188 | 195 | 202 | 209 | 216 | 222 | 229 | 236 | 243 |
| 71 | 136 | 143 | 150 | 157 | 165 | 172 | 179 | 186 | 193 | 200 | 208 | 215 | 222 | 229 | 236 | 243 | 250 |
| 72 | 140 | 147 | 154 | 162 | 169 | 177 | 184 | 191 | 199 | 206 | 213 | 221 | 228 | 235 | 242 | 250 | 258 |
| 73 | 144 | 151 | 159 | 166 | 174 | 182 | 189 | 197 | 204 | 212 | 219 | 227 | 235 | 242 | 250 | 257 | 265 |
| 74 | 148 | 155 | 163 | 171 | 179 | 186 | 194 | 202 | 210 | 218 | 225 | 233 | 241 | 249 | 256 | 264 | 272 |
| 75 | 152 | 160 | 168 | 176 | 184 | 192 | 200 | 208 | 216 | 224 | 232 | 240 | 248 | 256 | 264 | 272 | 279 |
| 76 | 156 | 164 | 172 | 180 | 189 | 197 | 205 | 213 | 221 | 230 | 238 | 246 | 254 | 263 | 271 | 279 | 287 |
Body Mass Index Table 2 of 2
| Obese | Extreme Obesity | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 | 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | ||
| Height
(inches) |
Body Weight (pounds) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 58 | 172 | 177 | 181 | 186 | 191 | 196 | 201 | 205 | 210 | 215 | 220 | 224 | 229 | 234 | 239 | 244 | 248 | 253 | 258 | ||
| 59 | 178 | 183 | 188 | 193 | 198 | 203 | 208 | 212 | 217 | 222 | 227 | 232 | 237 | 242 | 247 | 252 | 257 | 262 | 267 | ||
| 60 | 184 | 189 | 194 | 199 | 204 | 209 | 215 | 220 | 225 | 230 | 235 | 240 | 245 | 250 | 255 | 261 | 266 | 271 | 276 | ||
| 61 | 190 | 195 | 201 | 206 | 211 | 217 | 222 | 227 | 232 | 238 | 243 | 248 | 254 | 259 | 264 | 269 | 275 | 280 | 285 | ||
| 62 | 196 | 202 | 207 | 213 | 218 | 224 | 229 | 235 | 240 | 246 | 251 | 256 | 262 | 267 | 273 | 278 | 284 | 289 | 295 | ||
| 63 | 203 | 208 | 214 | 220 | 225 | 231 | 237 | 242 | 248 | 254 | 259 | 265 | 270 | 278 | 282 | 287 | 293 | 299 | 304 | ||
| 64 | 209 | 215 | 221 | 227 | 232 | 238 | 244 | 250 | 256 | 262 | 267 | 273 | 279 | 285 | 291 | 296 | 302 | 308 | 314 | ||
| 65 | 216 | 222 | 228 | 234 | 240 | 246 | 252 | 258 | 264 | 270 | 276 | 282 | 288 | 294 | 300 | 306 | 312 | 318 | 324 | ||
| 66 | 223 | 229 | 235 | 241 | 247 | 253 | 260 | 266 | 272 | 278 | 284 | 291 | 297 | 303 | 309 | 315 | 322 | 328 | 334 | ||
| 67 | 230 | 236 | 242 | 249 | 255 | 261 | 268 | 274 | 280 | 287 | 293 | 299 | 306 | 312 | 319 | 325 | 331 | 338 | 344 | ||
| 68 | 236 | 243 | 249 | 256 | 262 | 269 | 276 | 282 | 289 | 295 | 302 | 308 | 315 | 322 | 328 | 335 | 341 | 348 | 354 | ||
| 69 | 243 | 250 | 257 | 263 | 270 | 277 | 284 | 291 | 297 | 304 | 311 | 318 | 324 | 331 | 338 | 345 | 351 | 358 | 365 | ||
| 70 | 250 | 257 | 264 | 271 | 278 | 285 | 292 | 299 | 306 | 313 | 320 | 327 | 334 | 341 | 348 | 355 | 362 | 369 | 376 | ||
| 71 | 257 | 265 | 272 | 279 | 286 | 293 | 301 | 308 | 315 | 322 | 329 | 338 | 343 | 351 | 358 | 365 | 372 | 379 | 386 | ||
| 72 | 265 | 272 | 279 | 287 | 294 | 302 | 309 | 316 | 324 | 331 | 338 | 346 | 353 | 361 | 368 | 375 | 383 | 390 | 397 | ||
| 73 | 272 | 280 | 288 | 295 | 302 | 310 | 318 | 325 | 333 | 340 | 348 | 355 | 363 | 371 | 378 | 386 | 393 | 401 | 408 | ||
| 74 | 280 | 287 | 295 | 303 | 311 | 319 | 326 | 334 | 342 | 350 | 358 | 365 | 373 | 381 | 389 | 396 | 404 | 412 | 420 | ||
| 75 | 287 | 295 | 303 | 311 | 319 | 327 | 335 | 343 | 351 | 359 | 367 | 375 | 383 | 391 | 399 | 407 | 415 | 423 | 431 | ||
| 76 | 295 | 304 | 312 | 320 | 328 | 336 | 344 | 353 | 361 | 369 | 377 | 385 | 394 | 402 | 410 | 418 | 426 | 435 | 443 | ||
- Avoid crash diets. Instead, eat less of the foods you usually have. Limit the amount of fat you eat.
- Increase your physical activity. Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity most days of the week.
- Set a reasonable weight-loss goal, such as losing 1 pound a week. Aim for a long-term goal of losing 5 to 7 percent of your total body weight. To estimate this amount in pounds, find the weight closest to yours on the chart below. Follow the row across to see how many pounds you need to lose.
| Your weight in pounds | 5 percent loss in pounds | 7 percent loss in pounds |
|---|---|---|
| 150 | 8 | 11 |
| 175 | 9 | 12 |
| 200 | 10 | 14 |
| 225 | 11 | 16 |
| 250 | 13 | 18 |
| 275 | 14 | 19 |
| 21 |
||
| 325 | 16 | 23 |
| 350 |
Prediabetes
What is Prediabetes?
Prediabetes is a condition in which blood glucose or A1C levels—which reflect average blood glucose levels—are higher than normal but not high enough for a diagnosis of diabetes. Prediabetes is becoming more common in the United States. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services estimates that at least 84.1 million U.S. adults ages 18 or older had prediabetes in 2015.1 People with prediabetes are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes and CVD, which can lead to heart attack or stroke.Insulin
What is insulin?
Insulin is a hormone made in the pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach. The pancreas contains clusters of cells called islets. Beta cells within the islets make insulin and release it into the blood.Insulin plays a major role in metabolism—the way the body uses digested food for energy. The digestive tract breaks down carbohydrates—sugars and starches found in many foods—into glucose. Glucose is a form of sugar that enters the bloodstream. With the help of insulin, cells throughout the body absorb glucose and use it for energy.
Insulin's Role in Blood Glucose Control
When blood glucose levels rise after a meal, the pancreas releases insulin into the blood. Insulin and glucose then travel in the blood to cells throughout the body.- Insulin helps muscle, fat, and liver cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream, lowering blood glucose levels.
- Insulin stimulates the liver and muscle tissue to store excess glucose. The stored form of glucose is called glycogen.
- Insulin also lowers blood glucose levels by reducing glucose production in the liver.
Diabetes
Diabetes
Insulin resistance is a known risk factor for type 2 diabetes. It arises when the body's cells are no longer able to respond to , which is the hormone that regulates blood glucose.As a result, blood glucose levels can become too high, and this may lead to type 2 diabetes. There are medications that can help to prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes in patients with insulin resistance, such as thiazolidinediones.
But unfortunately, these medications can promote weight gain and a number of other health problems.
Dr. Domenico Accili — director of the Columbia University Diabetes Research Center at Columbia University Medical Center in New York City, NY — and colleagues have identified a number of compounds that may be just as effective as current insulin resistance medications on the market, but which do not lead to weight gain.
Friday, 27 October 2017
Why Is Diabetes On The Rise In Bangladesh?
Diabetes has become a national health concern in Bangladesh; however, treatment and control are quite low. Improving detection, awareness, and treatment strategies is urgently needed to prevent the growing burden associated with diabetes.
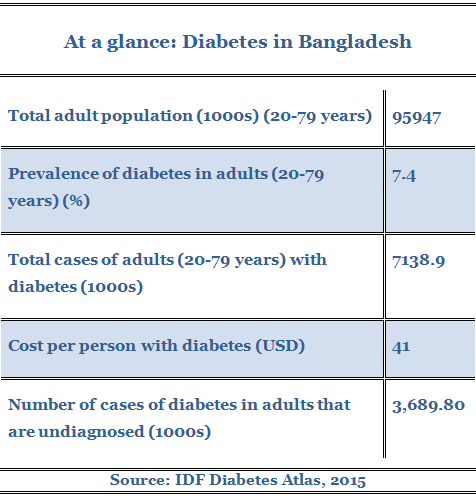 |
state of diabetes in Bangladesh |
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

